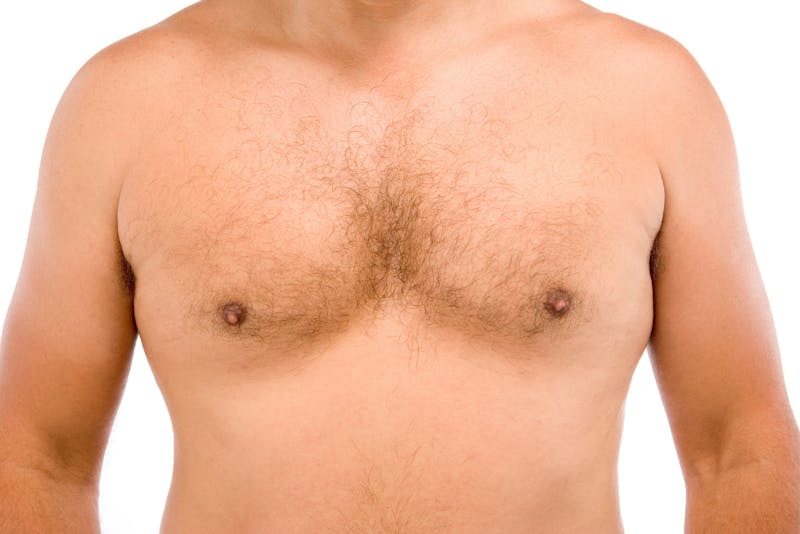
Gynecomastia is the abnormal development of tissues and glands in the male breast. This sometimes occurs during adolescence and clears up on its own with time, but some men experience gynecomastia later in life. This can be due to anything from hormonal imbalances to the use of certain medications.
Gynecomastia differs from regular chest fat in that it’s caused by excessive glandular breast tissue in the pectoral region. Fat can congregate in the chest due to weight gain and – unlike gynecomastia – it responds to diet and exercise. Gynecomastia, however, often requires surgical treatment.
If you are unsure whether you’re experiencing gynecomastia or regular chest fat, an appointment with a professional is the best means to determine the cause. Below, we will go over some of the common means of figuring out the difference between chest fat and gynecomastia.
Chest Fat Vs. Gynecomastia: Evaluating Symptoms
Are You Experiencing Pain?
Gynecomastia can cause mild to significant pain and tenderness in the chest area. Your chest may feel swollen, consistently sore, and painful to the touch. This is much less likely to occur with chest fast.
That being said, chest fat certainly can be painful for a variety of reasons unrelated to gynecomastia. This is why it is important to evaluate more than one factor when trying to differentiate between the two.
What Does The Fat Feel Like?
Chest fat will typically feel like fat anywhere else in the body, such as fat on the stomach, thighs, or arms. Chest fat is typically soft to the touch, while gynecomastia is much firmer.
Some patients describe gynecomastia as feeling hard or rubbery. In fact, you may even feel a solid lump underneath your skin, which does not typically occur with chest fat.
What Does Your Chest Look Like?
Chest fat often looks saggy or droopy and does not have a very defined shape. Gynecomastia, however, tends to be rounder and more proportioned. It may look similar to a woman’s breasts. In cases with smaller amounts of tissue, the nipple areolar complex may project more than the rest of the chest.
How Does Your Body React To Diet And Exercise?
One of the biggest indicators of whether you’re experiencing chest fat or gynecomastia is how your body responds to diet and exercise. While everyone’s body carries fat differently, and you may lose fat faster in certain areas, you should notice at least some reduction in the size of your pectoral region with weight loss.
If you notice little or zero change – even after significant weight loss – this is a tell-tale sign of gynecomastia. Sometimes with weight loss the glandular tissue becomes more evident because the fat around it that may have been hiding it is reduced.
Gynecomastia Treatment
While gynecomastia sometimes clears up on its own, it typically requires surgical treatment. Surgery can be performed under intravenous sedation or general anesthesia depending on patient needs.
In many cases, liposuction in addition to excision of glandular tissue may be necessary for proper contouring of the chest. In these cases, your surgeon will make a small incision in your skin and insert a thin tube called a cannula. Then, fat is removed from the body via suction. The glandular tissue can often be removed from the same incision. Even in minor cases, liposuction is rarely effective on its own.
For more severe cases, your surgeon may need to use what are called “excision techniques” in which they remove both glandular breast tissue and excess skin via a larger incision. This is also sometimes necessary if you want to reposition the nipple or areola during surgery to create a more natural-looking contour.
In many cases, reduction of volume of the chest can lead to some sagging skin. In many of these cases skin tightening therapies may be effective, such as Renuvion.
Before treatment, your surgeon will go over aftercare instructions with you, which you should follow closely to avoid complications. Most patients need at least one to two weeks of downtime following surgery.
Chest Fat Treatment
Sometimes, fat congregates in certain areas of the body due to genetics, and therefore does not respond to diet and exercise. In these cases, liposuction is still a viable option. However, more often than not, diet and exercise alone can treat chest fat.
When you lose weight, you should notice a reduction in fat in all areas of the body, including the chest. While spot reduction is a myth, toning your chest via weight training can reduce the appearance of fat. Incorporating exercises like chest flies and bench presses into your workout routine can help you achieve your aesthetic goals.
Chest Fat Vs. Gynecomastia: The Bottom Line
It can be difficult to differentiate between chest fat and gynecomastia, but there are some key indicators that can help you identify one over the other. However, always make an appointment with a professional for an official diagnosis, especially if you are experiencing troubling symptoms such as pain.
Seeking gynecomastia treatment? Leif Rogers is an Ivy League-educated, board-certified plastic surgeon and a standing member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons. If you’re considering surgery, get in touch with his team to schedule a consultation.


